# Genioplasty: chin reshaping
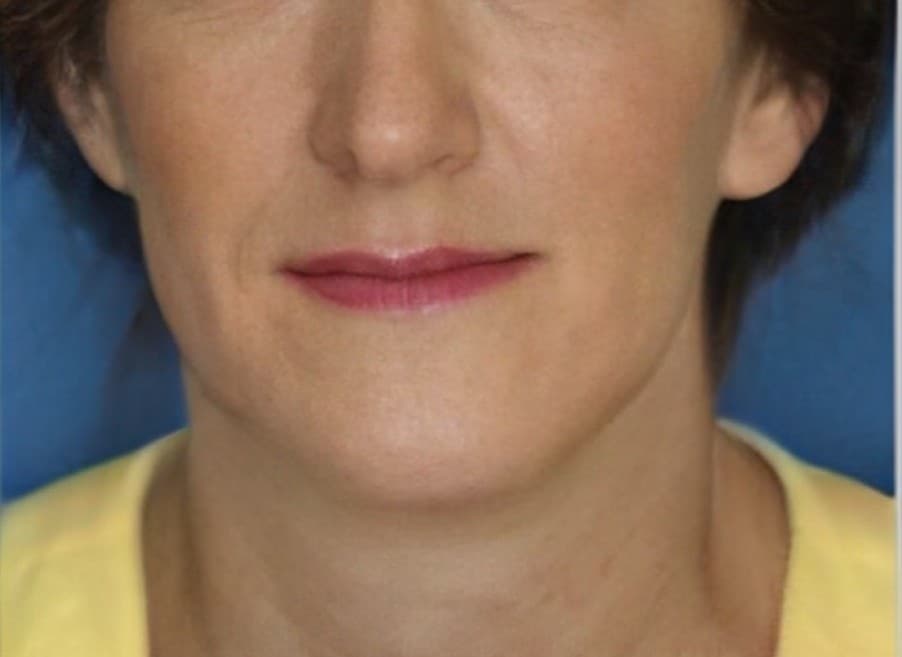
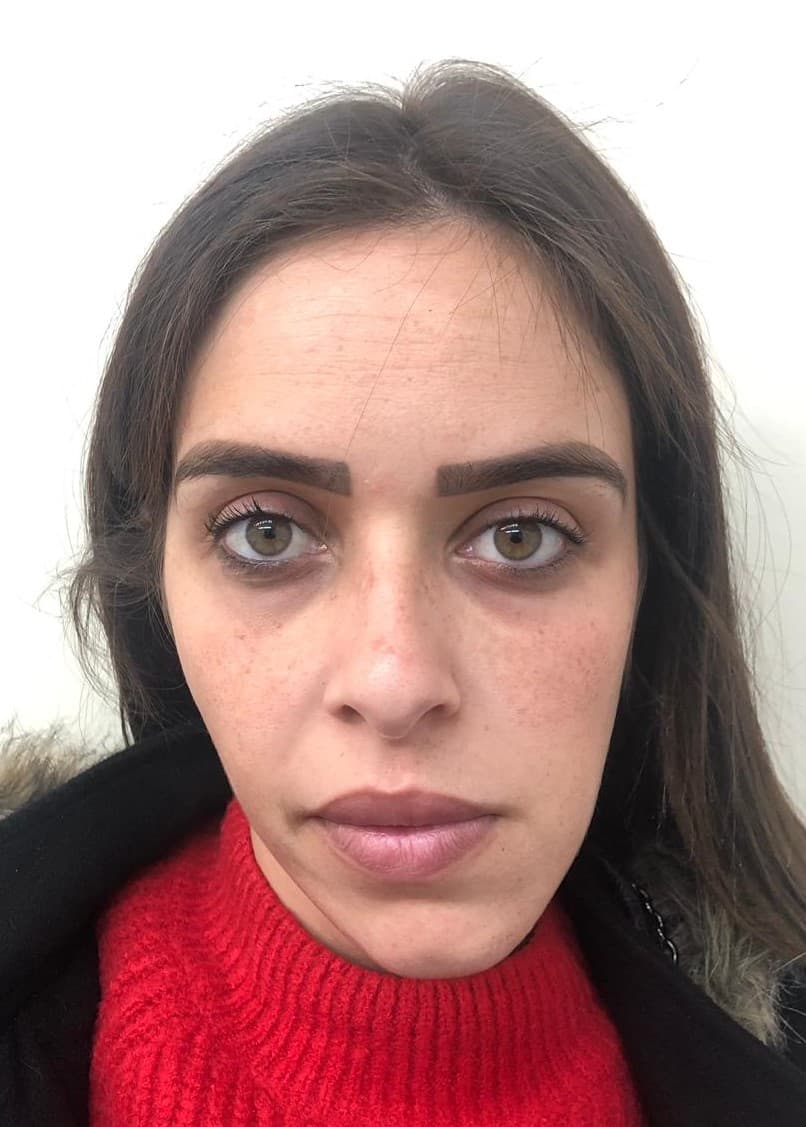
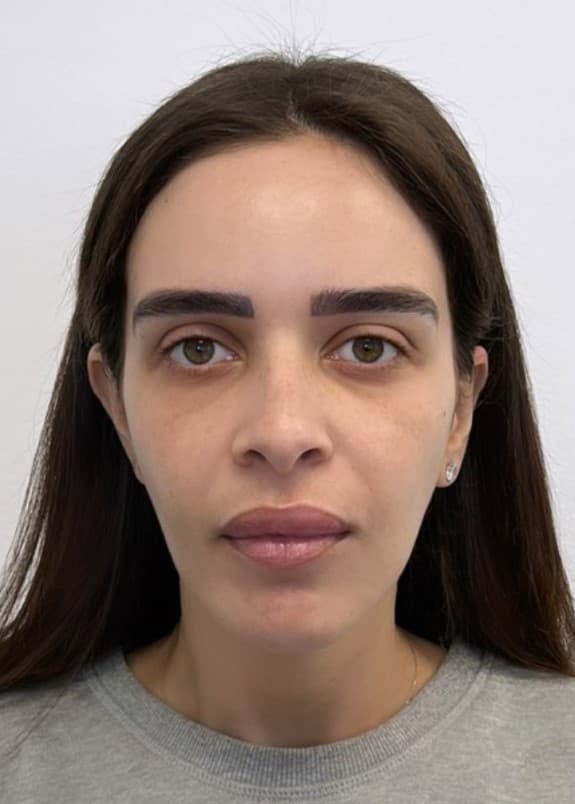
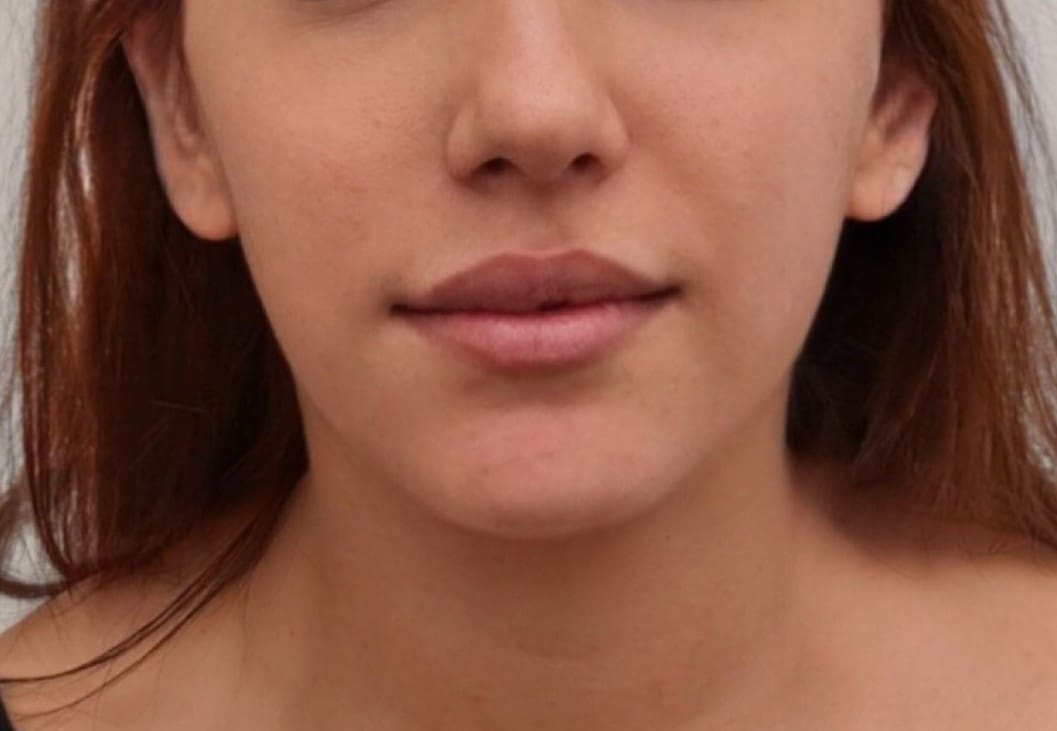
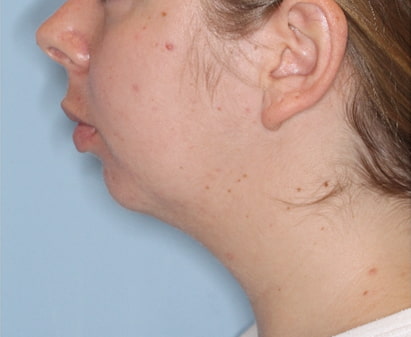
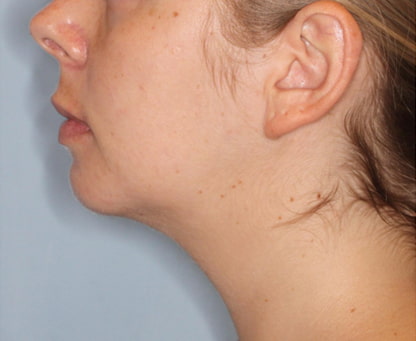
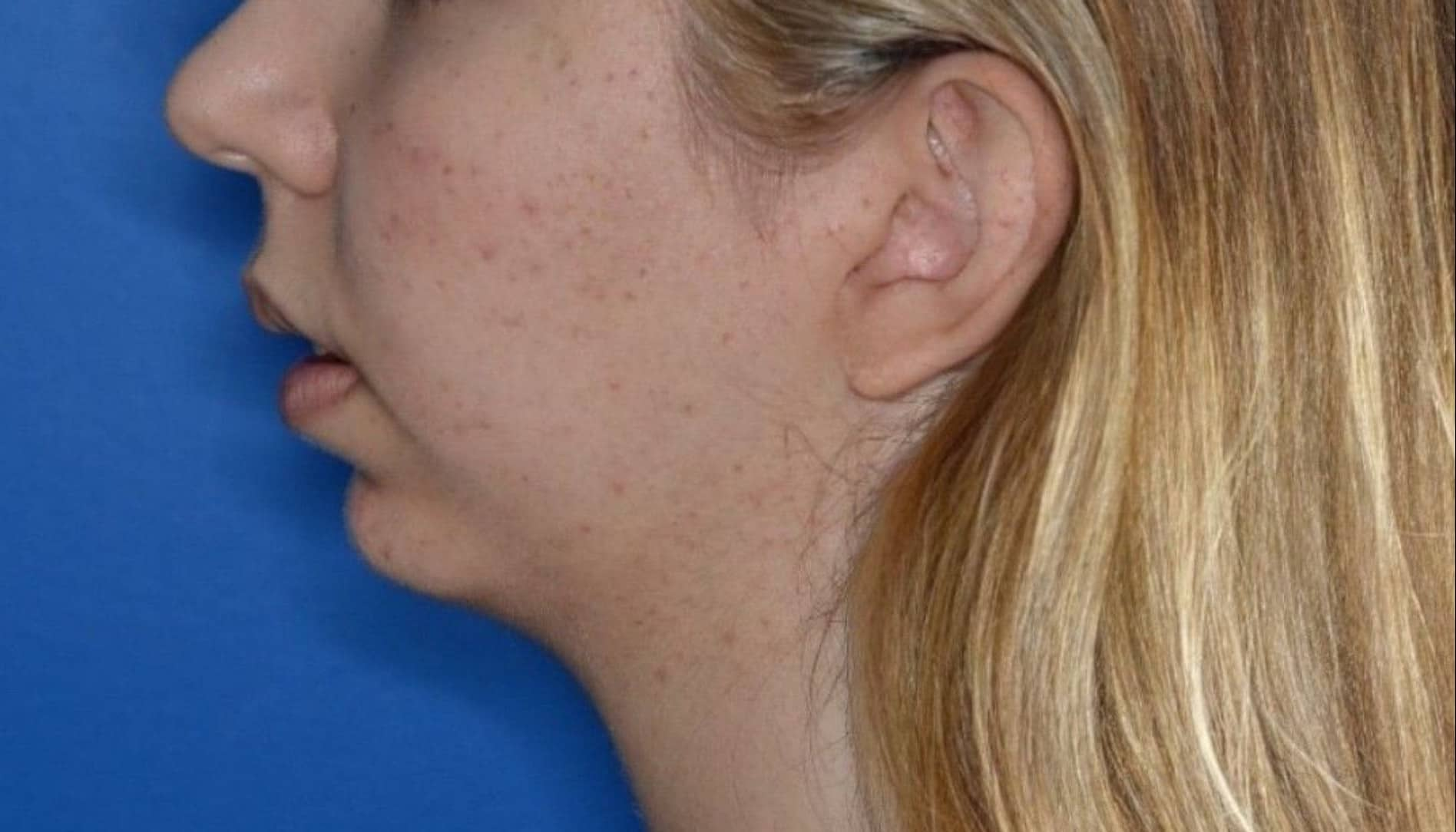
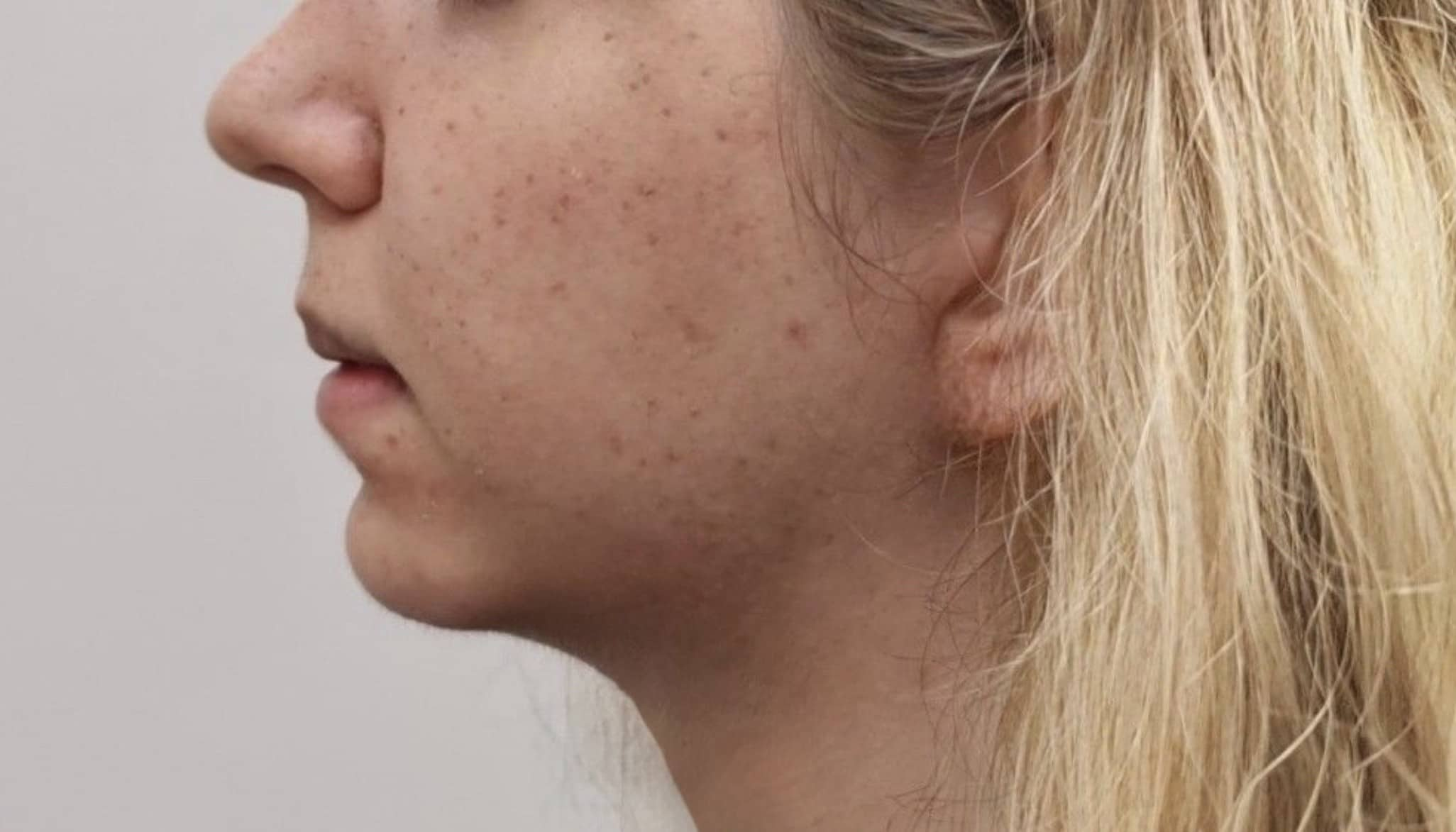
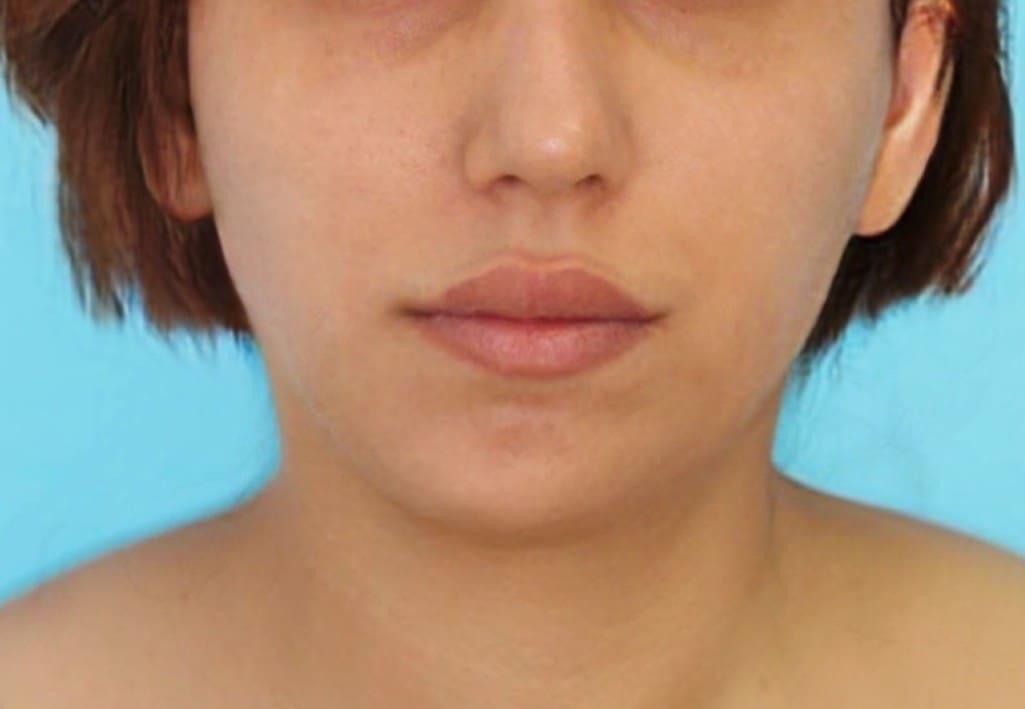
Genioplasty is a surgery that aims to change the appearance of the chin by reshaping it. The surgery is performed for aesthetic reasons to improve the appearance and profile of the face, or for medical reasons such as correcting asymmetry and deviation in the jaw position or defects in the jaw structure.
The history of this surgery begins in 1849, when an American surgeon named Simon P. Hullihen performed bony genioplasty for the first time. He developed the method in which a cut is made in the chin bone and then it is moved forward or backward, a technique that is still in use today.
Indications for genioplasty include a receding/backward (retrognathic) chin, an overly prominent (prognathic) chin, asymmetry/deviation or drooping of the jaw line following accidents, and congenital diseases or problems. In addition, there are patients who choose to undergo the surgery as a complementary procedure to other jaw surgeries or to improve the general appearance of the face.
# Genioplasty types
- Bony Genioplasty: This is the classic type of surgery developed by Dr. Hullihen over 170 years ago. In this procedure, the chin bone is cut and moved forward or backward as needed, and then fixed in place using fine screws and/or thin plates. This allows for a permanent change in the structure of the chin. The advantages of bony genioplasty include a long and proven medical history, full biological compatibility, and a stable, long-term change.
- Alloplastic Genioplasty (Genioplasty with Implant): This procedure involves the insertion of a synthetic implant, usually made of a polymer material, to improve the shape of the chin. The main advantage is the simplicity of the surgical procedure (compared to bony genioplasty). Another advantage is the ability to control the exact dimensions of the implant.
Both types of surgery are typically performed through an incision in the inner mucosa of the lower lip and do not require external cuts on the facial skin. The main surgical risks include bleeding, infection, changes in sensation in the lower lip and chin area, and, in rare cases, complications that may require further surgical intervention, such as removal of the fixation screws and/or implant.
After surgery, most patients experience swelling and pain during the first week. A return to normal activities is usually possible within four weeks, with final results visible after about two to three months, depending on the type of surgery and the patient's medical condition.